Manufacturing Account Format
المحتويات
Cost tracking is essential in calculating the correct profit margin of an item. Your profit margin is the percentage of profit you keep from each sale. Understanding your profit margins can help you determine whether or not your products are priced correctly and if your business is making money. For example, a plumber offers plumbing services but may also have inventory on hand to sell, such as spare parts or pipes. To calculate COGS, the plumber has to combine both the cost of labor and the cost of each part involved in the service. Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping.
Is the cost of goods sold an expense?
This method gives you the COGS for the period, reflecting the direct costs of goods that were sold. The above example shows how the cost of goods sold might appear in a physical accounting journal. The cost of goods sold and cost of sales refer to the same calculation. Both determine how much a company spent to produce their sold goods or services. As a brief refresher, your COGS is how much it costs to produce your goods or services. COGS is your beginning inventory plus purchases during the period, minus your ending inventory.
- It reflects the expenses accumulated during the manufacturing process, regardless of whether the goods are sold or not.
- The trading account is used to determine the gross profit on finished goods and is used by both trading and manufacturing businesses.
- Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping.
- In addition the manufacturing account format used in this example shows the cost of the raw materials consumed and the prime cost of manufacturing the products for the accounting period.
- It represents the total expense incurred during the production process within a specific period and enables you to assess the true cost of bringing products to market.
Work in process inventory
The trading profit and loss account of a manufacturing business is similar in format to that of a merchandising business except that purchases is replaced by the manufacturing cost of goods completed. We’ll assume for this example that all raw materials are direct materials, just to simplify the calculations. consignment sale definition By following this calculation, you can determine the total cost incurred to manufacture goods during a specified period and gain valuable insights into your production expenses. The COGS is deducted from your business revenue to determine the gross profit, which is then used to calculate taxable income.
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question
Working closely with manufacturers on case studies and peering deeply into a plethora of manufacturing topics, Mattias always makes sure his writing is insightful and well-informed. At the end of the quarter, $8,500 worth of furniture is still unfinished as calculated by the MRP system. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
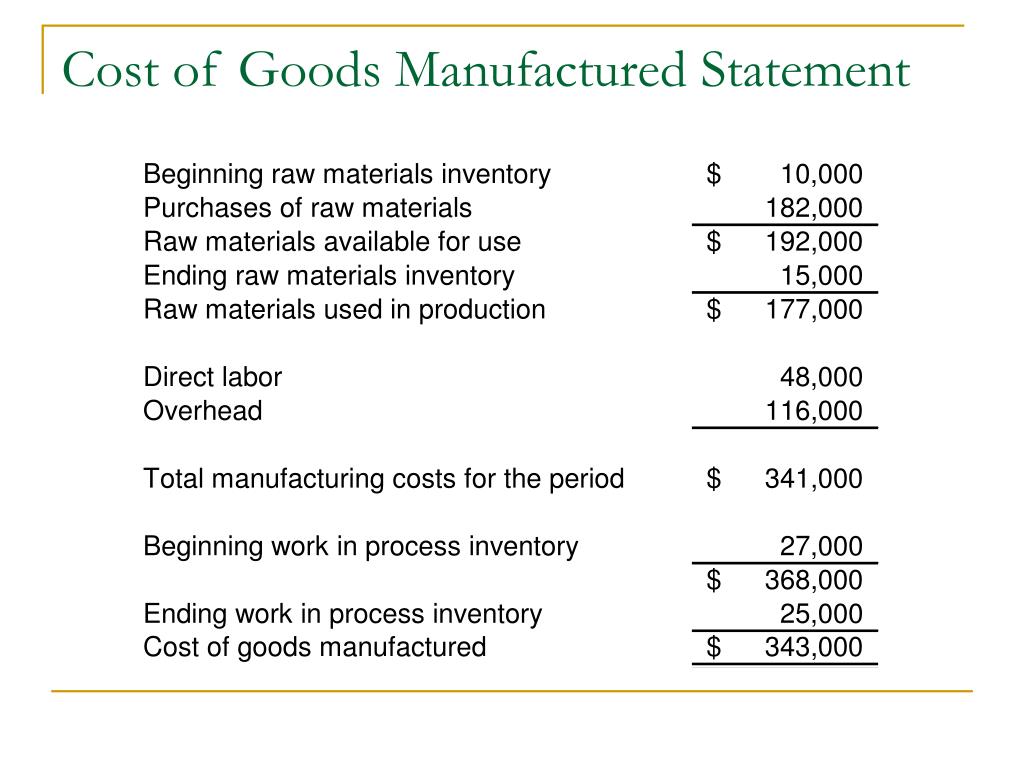
For a manufacturing business the balance brought down from the manufacturing account represents the manufacturing cost of goods completed (finished goods) for the accounting period. This cost is transferred to the trading account using a closing journal entry and is the equivalent to the purchases amount used by a merchandising or trading business. The manufacturing account is prepared by closing the temporary cost accounts and adjusting the raw materials (RM) and the work in process (WIP) inventory accounts using a closing journal entry as shown below. Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM) is a term used in managerial accounting that refers to a schedule or statement that shows the total production costs for a company during a specific period of time. Just like the name implies, COGM is the total cost incurred to manufacture products and transfer them into finished goods inventory for retail sale.

Here are the five steps for calculating COGS, then fill in our Cost of Goods Sold Calculator with your own data. When adding a COGS journal entry, debit your COGS Expense account and credit your Purchases and Inventory accounts. Inventory is the difference between your COGS Expense and Purchases accounts. If you don’t account for your cost of goods sold, your books and financial statements will be inaccurate.
Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting. Work in process (WIP) are products that are not yet ready for sale. Mattias is a content specialist with years of experience writing editorials, opinion pieces, and essays on a variety of topics. He is especially interested in environmental themes and his writing is often motivated by a passion to help entrepreneurs/manufacturers reduce waste and increase operational efficiencies. He has a highly informative writing style that does not sacrifice readability.
Beyond that, tracking accurate costs of your inventory helps you calculate your true inventory value, or the total dollar value of inventory you have in stock. Understanding your inventory valuation helps you calculate your cost of goods sold and your business profitability. Combining these numbers determine the total cost of services for your service business. This will help you understand the direct costs of providing your services and assess the profitability of your business operations. For a manufacturing business the manufacturing account needs to be prepared before completing the trading and profit and loss accounts.
Total costs incurred in the manufacturing process would then be $345,000 as shown below. The beginning WIP is the value of all unfinished products that carried over from the previous accounting period. The ending WIP, on the other hand, comprises the remaining manufacturing costs after deducting the value of goods finished within the period.
In other words, divide the total cost of goods purchased in a year by the total number of items purchased in the same year. There are other inventory costing factors that may influence your overall COGS. The IRS refers to these methods as “first in, first out” (FIFO), “last in, first out” (LIFO), and average cost. Credit your Inventory account for $2,500 ($3,500 COGS – $1,000 purchase). The use and preparation of the trading and profit and loss accounts are more fully discussed in our trading profit and loss account post. Here is a video review of how to complete a schedule of cost of goods manufactured.
It’s very similar to the cost of goods manufactured except that it doesn’t factor in work in process. Joint costs are the costs of both raw materials and conversion that cannot be separated. Joint cost allocation is the process by which joint costs are assigned to particular products produced in a process or department. In general, having the schedule for Cost of Goods Manufactured is important because it gives companies and management a general idea of whether production costs are too high or too low relative to the sales they are making. No matter how COGS is recorded, keep regular records on your COGS calculations.
